SSH Access
Now let’s see how you can access your BitssCloud account with all of its environments and containers or just a separate container via SSH.
- Direct Access to the Container
Note: SSH access is provided to the whole account but not a separate environment.
SSH Access to a BitssCloud Account
- Open the BitssCloud dashboard and navigate to the upper toolbar.
2. Click the Settings button.

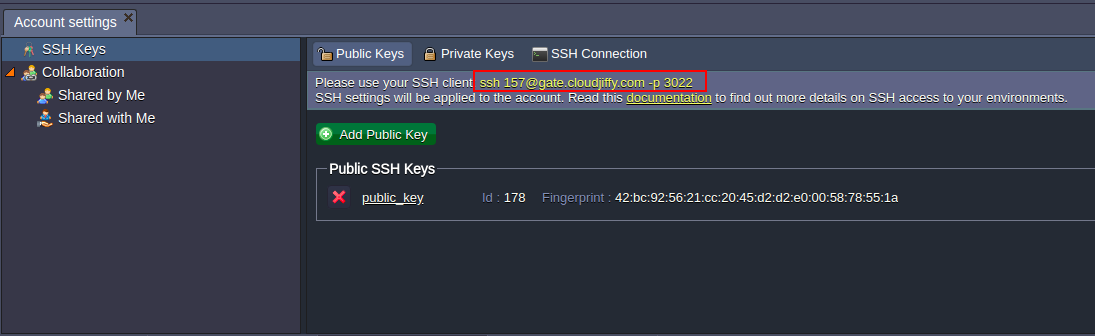
3. In the opened Account settings tab, navigate to the SSH Keychain > Public option.{Note: The availability of this option depends on your hosting provider’s settings. Usually, it is enabled for billing customers only.}
4. Click the link in the note to open your SSH gate. As a result, you’ll access Shell Handler via console automatically.
5. Or, just copy the given command line and run it via your console (SSH client).
For Linux/MacOS/FreeBSD
1. Open your terminal and enter SSH connection string from the Settings > SSH Keychain > Public tab at the dashboard.All the commands should be executed at your local machine’s user, similar to one you’ve used during SSH key pair generation, in order to avoid permission/connection errors.


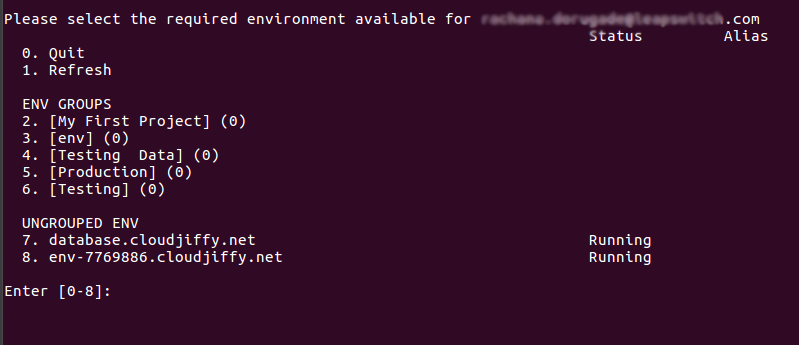
2. You will see a list of environments available for your account.
Please select the required environment by entering its list number.
Note: you can access only running environments.
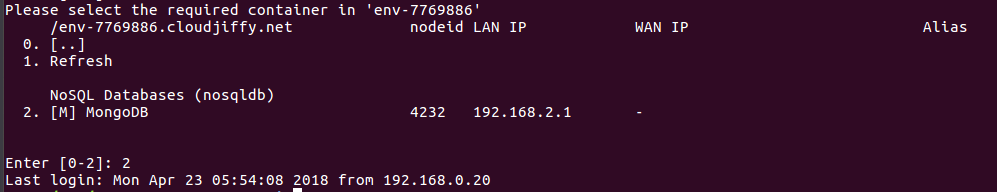
3. After that, you’ll see a full list of containers provisioned for the chosen environment.
Beside each container its node ID and LAN IP address are stated.
To access the container, enter its list number.
4. Now using shell assistance, you can proceed to setting the required configs.For Windows
1. To establish the SSH connection for Windows OS, you need to have a private key on your local machine which corresponds to the public one, previously added to the BitssCloud dashboard. Therefore, perform the following steps:
- Save a private version of your SSH key (we use PuTTY tools as an example):
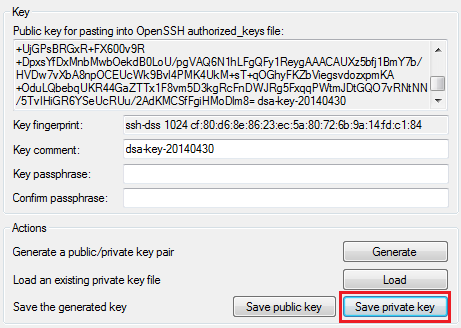
- Download and run PuTTY SSH agent (named Pageant). In the opened window click Add keybutton and navigate to your local file with private SSH key.
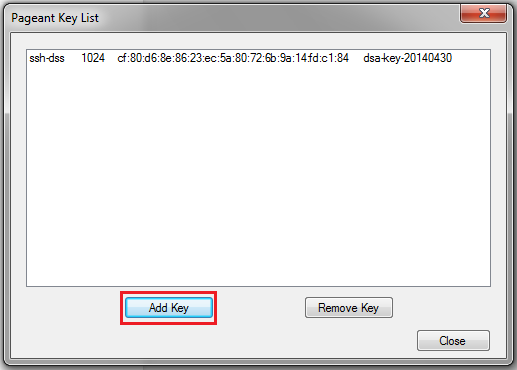
- Then you can press Close button. Pageant will be rolled to the tray. DO NOT exit this tool till SSH session closing, otherwise connection will be lost.
2. Download and run your SSH client (PuTTY as an example). Navigate to the Session tab in the left-hand list.
Fill in the Host Name (or IP address) field with your SSH connection string, that can be seen in the Settings > SSH Keychain > Public tab at the dashboard. Also specify 3022 Port number.
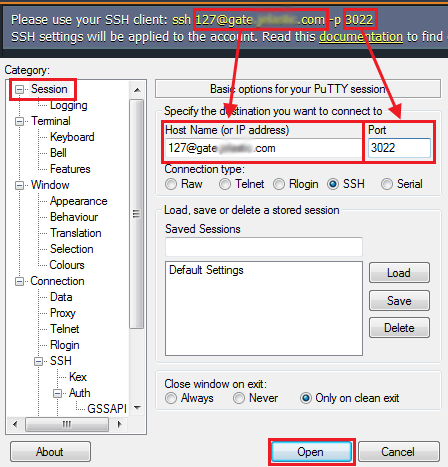
Press Open button.3. You’ll be shown the console with a list of environments available for your account. The further steps are similar to the ones for Linux/MacOS/FreeBSD OS.
Direct Access to the Container
You can also “jump” directly to the necessary container, skipping the steps of choosing appropriate environment and node.
To perform this, you need to know the required container ID. It can be retrieved using the previously described method of SSH access with interactive menu. There, you can see a list of all available containers and their ID numbers (the nodeid value).
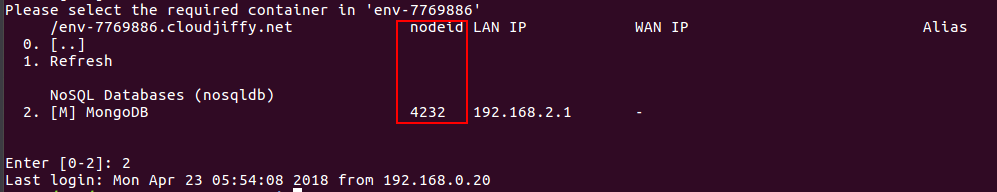
Use the nodeid value of the required container in the command of the following type:
ssh {nodeid}-{uid}@{SSH_gate} -p 3022
{uid} and {SSH_gateway} values are presented in the BitssCloud dashboard (Settings > SSH Keychain > Public).
For example, in order to access the MySQL-5.5.34 container in accordance with the gateway we use in this instruction, we need to enter the following command:
ssh 6481-97@gate.jelastic.com -p 3022
This option can be useful while working with tools for deployment and setting up configurations at the remote container. For example, such tools as Capistrano.
Note
- .bash_profile
This file is located in the container’s home directory (you enter it just after accessing the container) and contains the list of default variables. This file is not editable, so to set your own variables you need to state them in the .bashrc file (it is located in the same folder).
In order to define a new variable, write export VARNAME=VAR_VALUE in the abovementioned .bashrcfile, where:
VARNAME – name of the variable you would like to specify
VAR_VALUE – value of your variable
After you’ve set your variable, you can check it was applied. For that reenter the container and execute the next command:
echo $VARNAME
You should see the VAR_VALUE displayed, similar to one you’ve defined in the .bashrc file.
